👋 Hi, I’m Andre and welcome to my newsletter Data Driven VC which is all about becoming a better investor with Data & AI.
Join 45k+ readers from firms like a16z, Accel, Index, Sequoia, and more and get 30% off on all paid plans until New Year’s Eve
Brought to you by Affinity - The Leading Deal Intelligence
Affinity surveyed close to 300 private-capital professionals, and the message is clear: AI has crossed from experimentation to strategy. The use of AI for investment decisions has more than doubled YoY, while firms simultaneously consolidated their data stacks to 1–3 core sources.
Our 2026 Predictions report outlines how private capital investors are leveraging these shifts to source faster, and stand out in competitive processes.
Welcome to another Data Driven VC “Insights” episode where we cover the most interesting startup research & reports from the past week.
The State of VC & Why the Last 3 Years Break Out
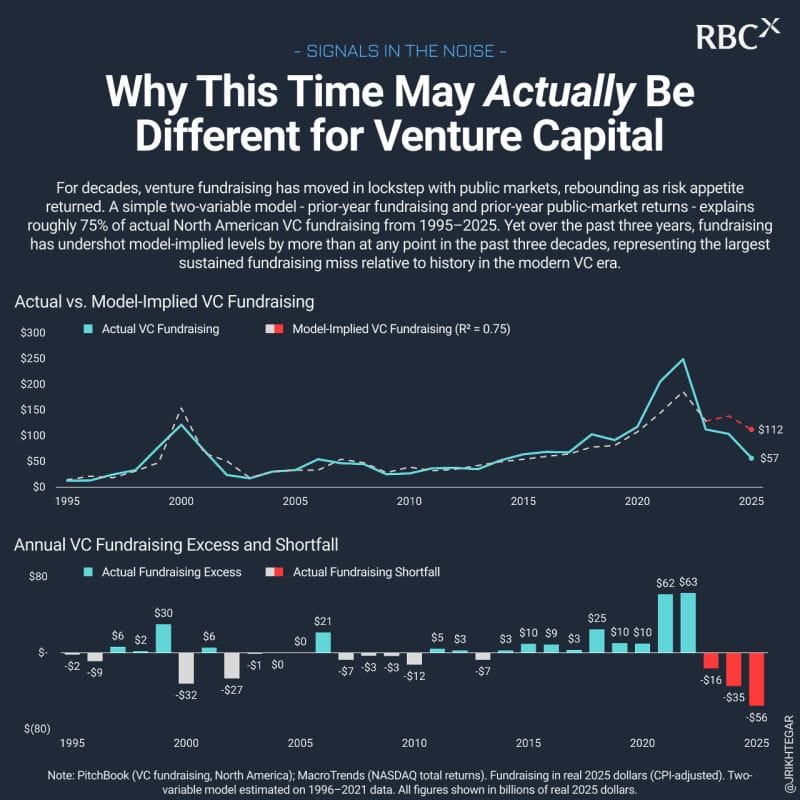
John Rikhtegar examines whether the last three years represent more than a normal venture downturn by testing a long-standing relationship between public markets and VC fundraising. His analysis shows that recent data deviates sharply from historical patterns that held for decades.
1995-2025 Regression with R² ~0.75: The article analyzes North American VC fundraising from 1995 to 2025 using prior-year fundraising and NASDAQ total returns as inputs. Historically, this simple model explained about 75% of annual fundraising outcomes.
NASDAQ +43.4%, +28.6%, +19.2% YTD vs VC Decline: Despite one of the strongest public-market stretches in decades, venture fundraising has continued to fall well below model predictions. The gap represents the largest and most persistent negative deviation in the full dataset, exceeding the dot-com crash and 2008 crisis.
3 Structural Explanations for the Divergence: Rikhtegar points to capital formation decoupling from risk appetite, liquidity constraints from weak DPI, and rising survivorship pressure on GPs. Together, these factors suggest a structural shift rather than a cyclical pause.
✈️ KEY TAKEAWAYS
The analysis suggests that venture fundraising is no longer reliably anchored to public market performance, signaling a structural reset where liquidity, selectivity, and credible paths to exits matter more than historical fundraising playbooks.

Lean Is the New Cool in Startup Hiring
This post by Peter Walker reflects on how startup status has shifted from headcount growth to operational efficiency. It combines commentary on contractors, early hiring choices, and recent Carta data to illustrate how founders are building teams today.
7 in 10 First Hires Are Engineers: Data from Carta shows that more than 70% of Hire #1 roles over the past two years have been engineers. This reinforces how technical execution remains the top early priority even as teams stay small.
Contractors vs Full-Time for Non-Core Roles: The author argues that many important but non-mission-critical roles can be effectively handled by contractors or fractional operators. This approach gives startups leverage without locking in long-term fixed costs too early.
Smaller Teams as a Status Signal: What once signaled success was hiring lots of people, now credibility comes from doing more with fewer employees. Lean org charts are increasingly seen as a feature, not a constraint.
✈️ KEY TAKEAWAYS
Early-stage startups are prioritizing technical talent and flexibility over headcount growth, using small teams and selective contractors to stay efficient while keeping core product development in-house.

Upgrade your subscription to access our premium content & join the Data Driven VC community

Unicorns Are Moving Faster but Exiting Differently
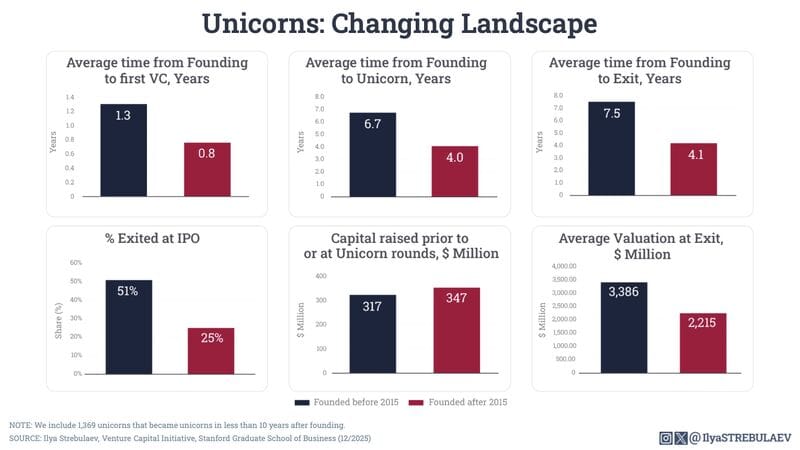
Ilya Strebulaev analyzes a large U.S. unicorn dataset to show how the lifecycle of venture-backed companies has shifted over the last decade. His comparison of pre- and post-2015 cohorts highlights a clear trade-off between speed and exit quality.
4.0 Years to Unicorn vs 6.7 Years Pre-2015: Companies founded after 2015 reached unicorn status in an average of 4 years, compared to 6.7 years for earlier cohorts. Time to the first VC round also shortened from 1.30 years to 0.8 years.
4.1 Years to Exit vs 7.5 Years Historically: Exited unicorns in the post-2015 cohort reached exits in nearly half the time of older peers. However, fewer recent unicorns exit at all, making these timelines conditional on successful exits.
IPO Share Down from 51% to 25%, Exit Value Down to $2.2B: The share of unicorns exiting via IPO fell by half, while average exit valuations declined from $3.4B to $2.2B. At the same time, capital raised through the unicorn round increased to $347M from $317M.
✈️ KEY TAKEAWAYS
The data suggests that newer unicorns optimize for speed but face weaker exit outcomes, raising more capital faster while seeing fewer IPOs and lower exit valuations, signaling a structural shift in how value is created and realized.

Vesting Cliffs Are Being Reconsidered, Not Abandoned
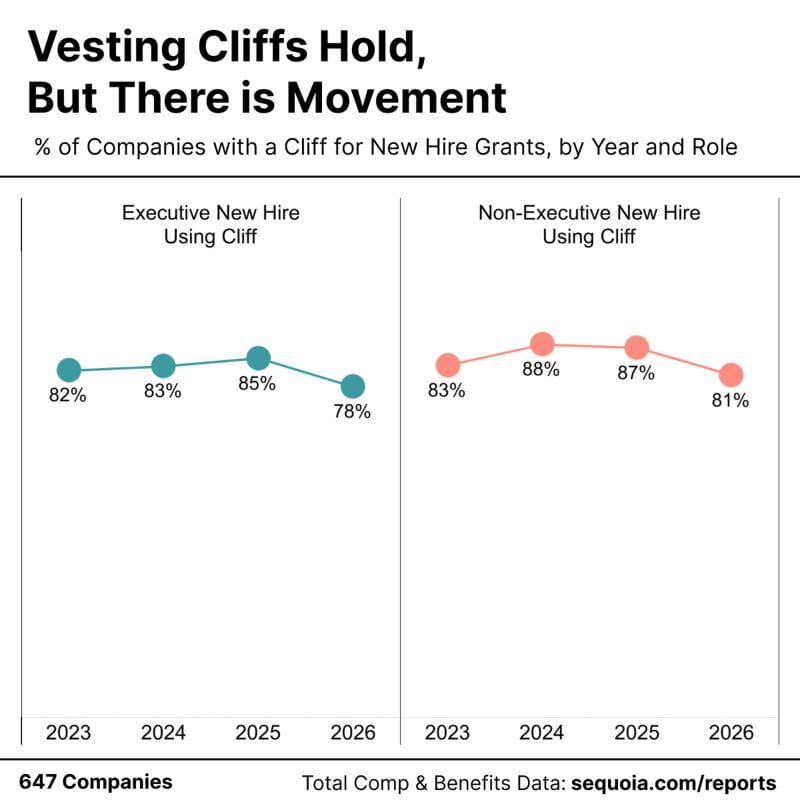
Dylan Hughes looks at recent changes in equity vesting practices following OpenAI’s move to cut vesting cliffs. He places the shift in the context of tighter hiring and capital discipline rather than a wholesale rethink of equity norms.
6-Month and 12-Month Cliffs Show a Small Pullback: The analysis notes a modest decline in the use of both 6-month and 1-year vesting cliffs over the past year. Cliffs remain the default, but the data suggests some companies are actively re-evaluating when ownership should begin.
OpenAI Example Highlights a Broader Pattern: OpenAI’s decision is framed as notable but not isolated. A small group of companies is testing alternatives, signaling early pressure points rather than a widespread reversal.
Earlier Equity Shifts Risk to Performance Management: Removing a cliff does not eliminate risk, it shifts ownership earlier in the employment relationship. That change increases the importance of early performance feedback and faster exit decisions.
✈️ KEY TAKEAWAYS
Vesting cliffs are still standard, but selective hiring, tighter capital, and closer scrutiny of equity outcomes are pushing some companies to question whether traditional 6- or 12-month cliffs still align with how they manage risk today.

Join our free Slack group as we automate our VC job end-to-end with AI. Live experiment. Full transparency.

Expensive Startups Don’t Outperform
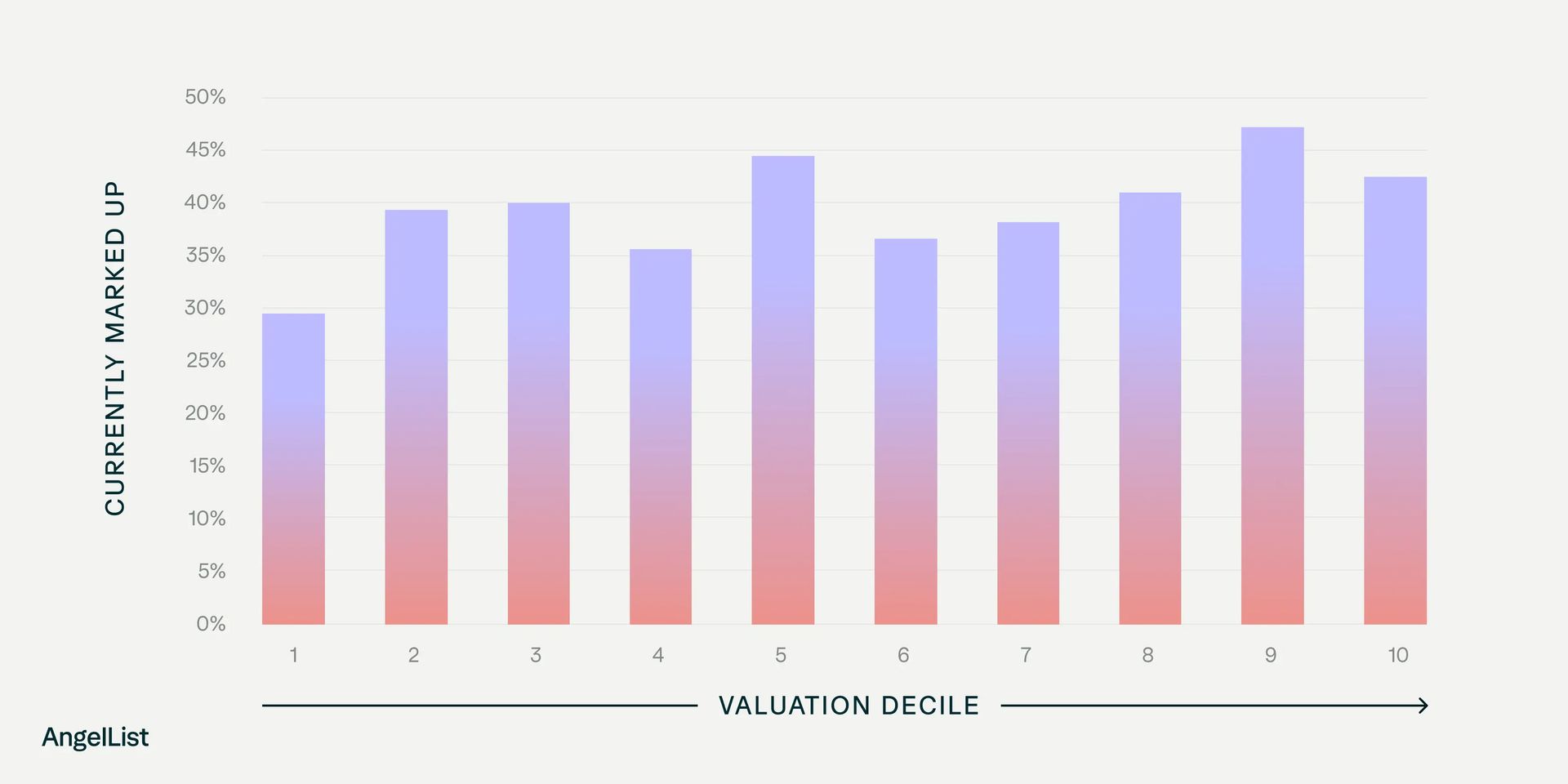
In a recent blog post, AngelList analyzed whether the most expensive Seed rounds truly outperform the rest of the market by replicating PitchBook’s claim using real-time, non-survivorship-biased data. The conclusion challenges the idea that paying up at Seed meaningfully improves outcomes.
54.9% vs 48.5% Markup Rates: Top-decile Seed rounds see a 54.9% chance of ever being marked up versus 48.5% for the rest of the market. The uplift exists, but it is far smaller than the 20+ point gap previously reported.
42.2% vs 29.4% Markups Across Valuation Deciles: Marked-up rates rise gradually from 29.4% in the cheapest decile to 42.2% in the most expensive. The slope is real but gentle, suggesting no sharp advantage for consensus pricing.
0 Correlation With 10x Winners: Deals achieving ≥10x MOIC are spread randomly across valuation deciles. Top-decile Seed rounds rank only fifth in producing outliers, while bottom-decile rounds are close behind.
✈️ KEY TAKEAWAYS
Consensus Seed rounds are slightly better on average, but they do not dominate outcomes. Higher prices reflect real signals, yet those signals are mostly priced in, and the biggest venture returns remain unpredictable across the valuation spectrum.

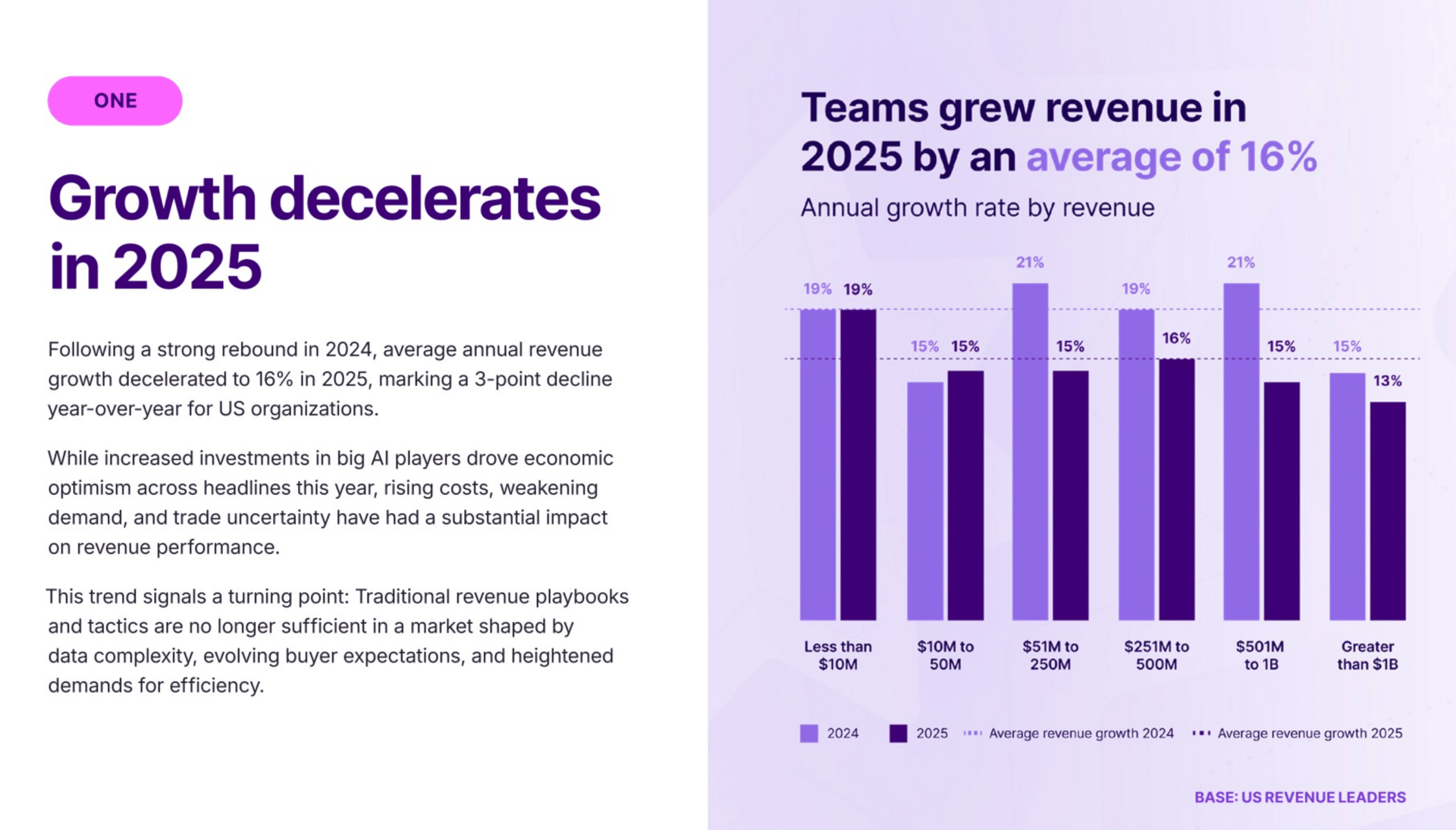
What Top Revenue Teams Did Differently in 2025
Gong’s State of Revenue AI report shows how high-performing revenue teams adapted to slower growth and widespread AI adoption. The data highlights a shift from expansion and tooling experiments toward productivity, leverage, and deeper workflow changes.
16% Growth and Revenue per Rep Focus: With average revenue growth slowing to around 16%, leading teams stopped relying on expansion and headcount. They prioritized output per rep and increased shots on goal, recognizing performance dropped mainly due to fewer opportunities worked.
30% Faster Growth With Deep AI Embedding: Teams that embedded AI directly into forecasting, deal reviews, and planning grew about 30% faster than those running pilots. Note-taking and content automation delivered marginal gains, while decision intelligence drove system-wide impact.
77% More Revenue per Rep From Frequent AI Use: Frequent AI users generated roughly 77% more revenue per rep than non-users. Domain-specific revenue AI also outperformed general-purpose tools, delivering about 13% higher growth.
✈️ KEY TAKEAWAYS
The best revenue teams treated productivity as a core product and assumed AI was table stakes. Real differentiation came from rebuilding workflows, trusting AI as a thinking partner, and measuring leverage through revenue per rep rather than efficiency or time saved.

Thanks to Lea Winkler for her help with this post.
Stay driven,
Andre
PS: Enjoying our content? Get 30% limited time discount on all paid plans until New Year’s Eve here